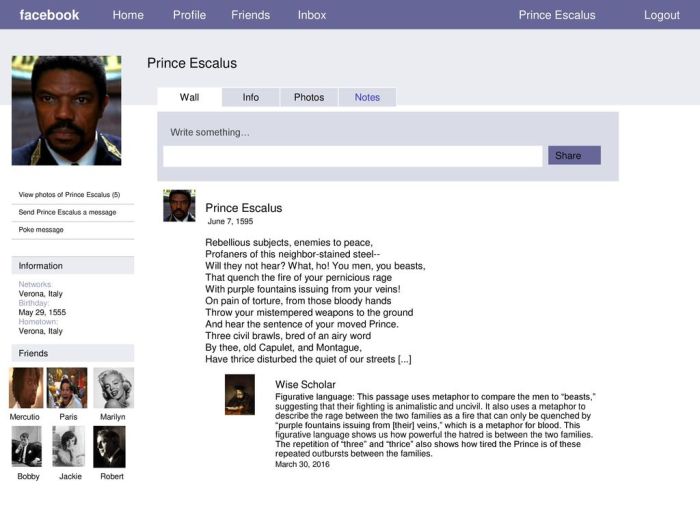
Rebellious subjects enemies to peace sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The concept of rebellious subjects and their impact on peace has been a subject of fascination and debate for centuries, and this work delves deeply into the motivations, consequences, and strategies for managing such individuals.
Throughout history, rebellious subjects have emerged in various forms, from political dissidents to religious zealots. Their actions have ranged from peaceful protests to violent uprisings, and their impact on society has been profound. This work explores the factors that drive individuals to rebel, the challenges governments face in dealing with them, and the strategies that have been employed to manage rebellious subjects both peacefully and coercively.
Rebellious Subjects: Definition and Characteristics

Rebellious subjects are individuals or groups who actively oppose or resist authority, often challenging established norms, laws, or political systems. They are characterized by a sense of grievance, a belief in their own righteousness, and a willingness to engage in disruptive or violent behavior.
Throughout history, rebellious subjects have emerged in various forms, including revolutionaries seeking political change, religious dissidents challenging established dogma, and social activists fighting for justice. Their motivations may stem from perceived injustice, oppression, or a desire for greater autonomy.
Enemies to Peace: The Impact of Rebellion, Rebellious subjects enemies to peace
Rebellion poses a significant threat to peace and social stability. It can lead to widespread violence, disrupt economic activity, and undermine the rule of law. Rebellions can also exacerbate existing inequalities, foster mistrust, and create a cycle of violence that is difficult to break.
For governments, dealing with rebellious subjects presents a complex challenge. They must balance the need to maintain order and protect the rights of citizens with the need to address the underlying grievances that fuel rebellion.
Managing Rebellious Subjects: Strategies and Approaches
| Strategy | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Peaceful Negotiation | Engaging in dialogue with rebellious subjects to address grievances and seek common ground. | Negotiations between the ANC and the apartheid government in South Africa |
| Coercive Force | Using military or police force to suppress rebellion and restore order. | The use of force to quell the Boxer Rebellion in China |
| Economic Incentives | Providing economic opportunities and resources to address underlying causes of rebellion. | The Marshall Plan to rebuild Europe after World War II |
| Social Inclusion | Promoting social cohesion and reducing marginalization to prevent rebellion. | Affirmative action policies in the United States |
Case Studies of Rebellious Subjects and Peace
Examining historical and contemporary case studies can provide valuable insights into the dynamics of rebellion and its impact on peace.
- The American Revolution: A successful rebellion that led to the establishment of a new nation.
- The Russian Revolution: A violent uprising that resulted in a communist regime.
- The Arab Spring: A series of uprisings that challenged authoritarian regimes in the Middle East.
Preventing Rebellion: Education, Economic Opportunity, and Social Inclusion
Addressing the root causes of rebellion is crucial for preventing its occurrence. Education, economic opportunity, and social inclusion play a vital role in fostering a more peaceful and just society.
- Education empowers individuals with critical thinking skills and provides them with a sense of purpose.
- Economic opportunity reduces poverty and inequality, addressing a major grievance that can fuel rebellion.
- Social inclusion fosters a sense of belonging and reduces marginalization, creating a more cohesive society.
FAQ: Rebellious Subjects Enemies To Peace
What are the main causes of rebellion?
The causes of rebellion are complex and varied, but some common factors include political oppression, economic inequality, social injustice, and religious extremism.
What are the consequences of rebellion?
Rebellion can have a devastating impact on society, leading to violence, social unrest, economic disruption, and political instability.
What are the different strategies for managing rebellious subjects?
There are a variety of strategies for managing rebellious subjects, including peaceful methods such as negotiation and dialogue, and coercive methods such as force and imprisonment.