Periodic table of elements quiz 1 36 – Embark on a journey through the Periodic Table of Elements Quiz 1-36, where we unravel the intricacies of the fundamental building blocks of our universe. This comprehensive guide delves into the history, structure, and properties of the first 36 elements, providing a foundation for understanding the chemical world around us.
As we explore the periodic table, we will uncover the periodic trends that govern the behavior of elements, enabling us to predict their chemical properties and reactivity. Furthermore, we will delve into the fascinating applications of these elements in science and technology, showcasing their indispensable role in shaping our modern world.
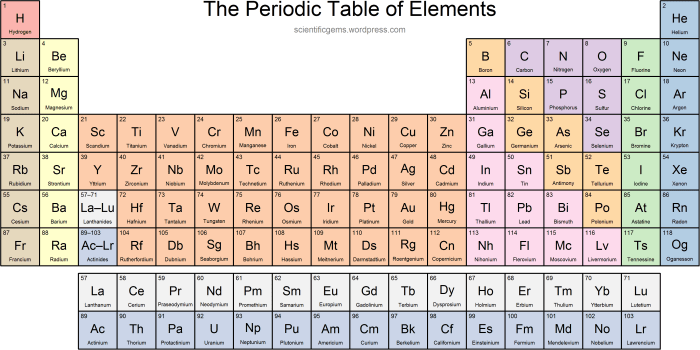
Periodic Table of Elements Quiz 1-36
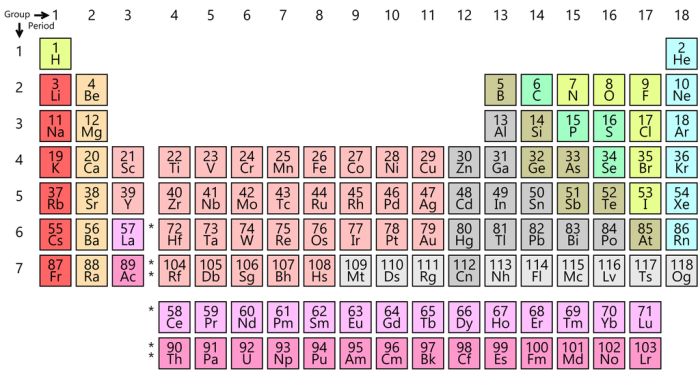
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, organized on the basis of their atomic number, electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. It is generally accepted that the modern periodic table was first published by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869, although several other scientists had developed similar tables prior to this.The
periodic table is divided into 18 vertical columns, called groups, and 7 horizontal rows, called periods. The groups are numbered 1-18 from left to right, and the periods are numbered 1-7 from top to bottom. The elements in the periodic table are arranged in such a way that elements with similar chemical properties are grouped together.
For example, all of the alkali metals (Group 1) are highly reactive and form 1+ ions, and all of the noble gases (Group 18) are unreactive and form no ions.
Properties and Trends
The periodic table can be used to predict the chemical properties of elements based on their position in the table. For example, elements in the same group tend to have similar chemical properties, and elements in the same period tend to have similar atomic radii.Some
of the most important periodic trends include:*
-*Atomic radius
The atomic radius of an element is the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Atomic radius generally increases down a group and decreases across a period.
-
-*Ionization energy
The ionization energy of an element is the energy required to remove an electron from the atom. Ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
-*Electronegativity
The electronegativity of an element is a measure of its ability to attract electrons. Electronegativity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.
Reactivity and Chemical Bonding
The reactivity of an element is a measure of its tendency to undergo chemical reactions. The reactivity of elements generally increases down a group and decreases across a period.The type of chemical bond that an element forms depends on its electronegativity.
Elements with high electronegativity tend to form ionic bonds, while elements with low electronegativity tend to form covalent bonds.Some of the most common types of chemical bonds include:*
-*Ionic bonds
Ionic bonds are formed between atoms with a large difference in electronegativity. In an ionic bond, one atom donates an electron to the other atom, resulting in the formation of two oppositely charged ions.
-
-*Covalent bonds
Covalent bonds are formed between atoms with a small difference in electronegativity. In a covalent bond, the atoms share one or more pairs of electrons.
-*Metallic bonds
Metallic bonds are formed between metal atoms. In a metallic bond, the metal atoms share their valence electrons in a sea of electrons.
Applications in Science and Technology, Periodic table of elements quiz 1 36
The elements in the periodic table are used in a wide variety of applications in science and technology. For example, the alkali metals are used in batteries, the alkaline earth metals are used in fertilizers, and the transition metals are used in catalysts.Some
of the most common applications of the elements in the periodic table include:*
-*Alkali metals
The alkali metals are used in batteries, fuel cells, and as catalysts.
-
-*Alkaline earth metals
The alkaline earth metals are used in fertilizers, cement, and glass.
-*Transition metals
The transition metals are used in catalysts, magnets, and alloys.
-*Lanthanides
The lanthanides are used in lasers, phosphors, and magnets.
-*Actinides
The actinides are used in nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons.
Query Resolution: Periodic Table Of Elements Quiz 1 36
What is the significance of the periodic table?
The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties, providing a systematic framework for understanding and predicting the behavior of elements.
How can I use the periodic table to predict the reactivity of an element?
The periodic table can be used to identify trends in reactivity based on an element’s position within the table. For example, elements in the same group tend to exhibit similar chemical properties and reactivity.
What are some real-world applications of the elements in the first 36 positions of the periodic table?
Elements such as hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen are essential for life on Earth and are used in a wide range of applications, including energy production, medicine, and manufacturing.