The Federal in Federalism Venn Diagram Answer Key is an indispensable resource for understanding the intricate relationship between federal, state, and local governments in a federal system. This diagram provides a visual representation of the overlapping and distinct powers of each level of government, offering a clear and concise explanation of the complexities of federalism.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the key principles and characteristics of federal systems, exploring the powers and responsibilities of each level of government. We will examine real-world examples of federalism in practice, discussing its benefits and challenges. Furthermore, we will trace the historical development of federalism and explore its potential future in the face of globalization and other challenges.
1. Define Federalism
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central authority and constituent political units (such as states or provinces). Each level of government has its own powers and responsibilities, and there is a system of checks and balances to prevent any one level of government from becoming too powerful.
The key principles of federalism include:
- The division of power between the central government and the constituent units.
- The supremacy of the central government in certain areas, such as foreign policy and defense.
- The autonomy of the constituent units in other areas, such as education and healthcare.
- A system of checks and balances to prevent any one level of government from becoming too powerful.
2. The Federal Government
The federal government is the central authority in a federal system. It is responsible for matters that affect the entire country, such as foreign policy, defense, and the economy. The federal government also has the power to make laws that apply to the entire country.
Some examples of federal government institutions and agencies include:
- The President
- The Congress
- The Supreme Court
- The Federal Reserve
- The Department of Defense
- The Department of Justice
3. State and Local Governments: The Federal In Federalism Venn Diagram Answer Key
State and local governments are the constituent units in a federal system. They are responsible for matters that affect their own citizens, such as education, healthcare, and law enforcement. State and local governments also have the power to make laws that apply to their own citizens.
The relationship between federal, state, and local governments is complex and ever-evolving. However, the general principle is that the federal government is supreme in matters of national importance, while state and local governments are autonomous in matters of local importance.
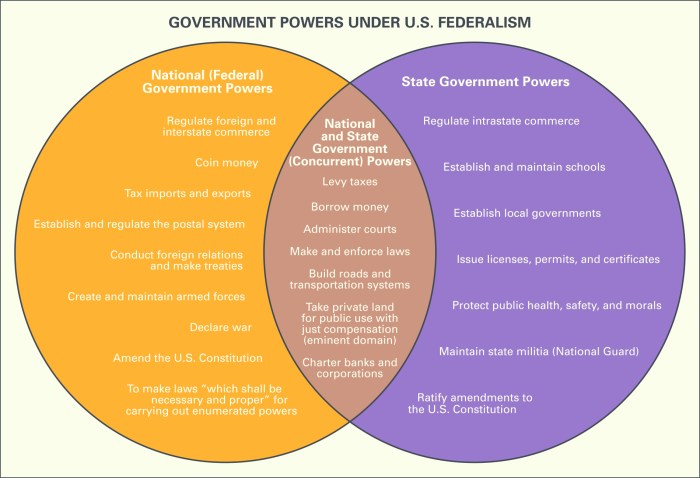
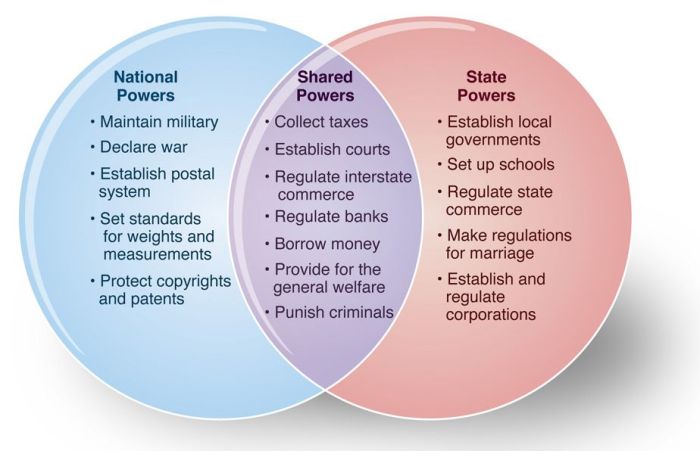
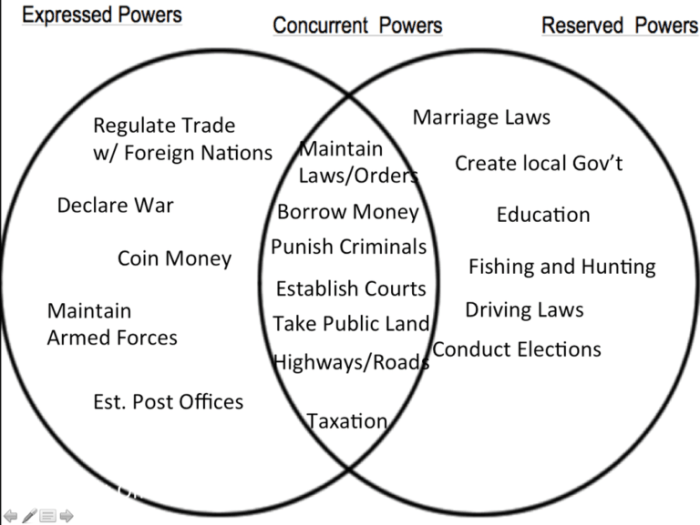
4. Venn Diagram Analysis
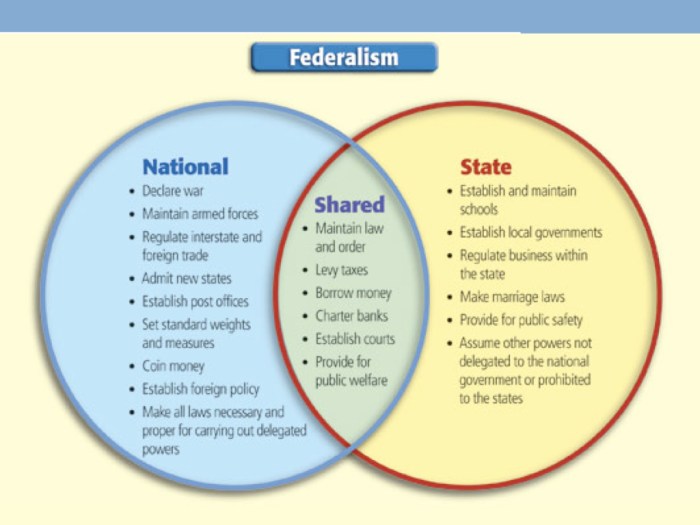
A Venn diagram can be used to illustrate the overlapping and distinct powers of the federal, state, and local governments.
The following Venn diagram shows the overlapping and distinct powers of the federal, state, and local governments:

Key:
- The blue circle represents the powers of the federal government.
- The red circle represents the powers of the state governments.
- The green circle represents the powers of the local governments.
- The overlapping area represents the powers that are shared by two or more levels of government.
5. Examples of Federalism in Practice
Federalism is a common form of government around the world. Some examples of federal systems include:
- The United States
- Canada
- Australia
- Germany
- Switzerland
Federalism can be a complex system of government, but it can also be very effective. By dividing power between different levels of government, federalism can help to prevent any one level of government from becoming too powerful.
6. Historical Development of Federalism
Federalism has a long and complex history. The concept of federalism first emerged in the United States in the late 18th century. The Founding Fathers of the United States were inspired by the ideas of the Enlightenment, which emphasized the importance of individual liberty and limited government.
The United States Constitution, which was adopted in 1789, established a federal system of government. The Constitution divides power between the federal government and the state governments. The federal government is responsible for matters of national importance, such as foreign policy and defense.
The state governments are responsible for matters of local importance, such as education and healthcare.
The United States federal system has been a model for other federal systems around the world. Today, there are over 20 federal systems in the world.
7. Comparative Federalism
Comparative federalism is the study of federal systems in different countries. Comparative federalism can help us to understand the different ways that federalism can be implemented and the different challenges that federal systems face.
Some of the key similarities and differences between federal systems include:
- The division of power between the central government and the constituent units.The division of power can vary from system to system. In some systems, the central government has more power than the constituent units. In other systems, the constituent units have more power than the central government.
- The role of the judiciary.The judiciary can play a different role in federal systems. In some systems, the judiciary is responsible for interpreting the constitution and resolving disputes between the central government and the constituent units. In other systems, the judiciary has a more limited role.
- The level of regional autonomy.The level of regional autonomy can vary from system to system. In some systems, the constituent units have a high degree of autonomy. In other systems, the constituent units have a more limited degree of autonomy.
8. Future of Federalism
The future of federalism is uncertain. Some experts believe that federalism is a dying form of government. They argue that the forces of globalization and regionalism are making it increasingly difficult for federal systems to function effectively.
Other experts believe that federalism is still a viable form of government. They argue that federalism can provide a way to accommodate diversity and to protect individual rights. They also argue that federalism can be a way to promote economic growth and development.
Only time will tell what the future holds for federalism. However, it is clear that federalism is a complex and adaptable form of government. It is a system that has been able to survive and thrive in a variety of different environments.
Essential FAQs
What is the main purpose of a federal system?
The main purpose of a federal system is to distribute power between a central government and multiple regional or state governments, allowing for both local autonomy and national unity.
What are the key characteristics of a federal system?
Key characteristics of a federal system include a written constitution, a division of powers between different levels of government, and a supreme court to interpret the constitution and resolve disputes.
What are the advantages of a federal system?
Advantages of a federal system include increased local autonomy, protection of minority rights, and the ability to accommodate diverse interests and needs.