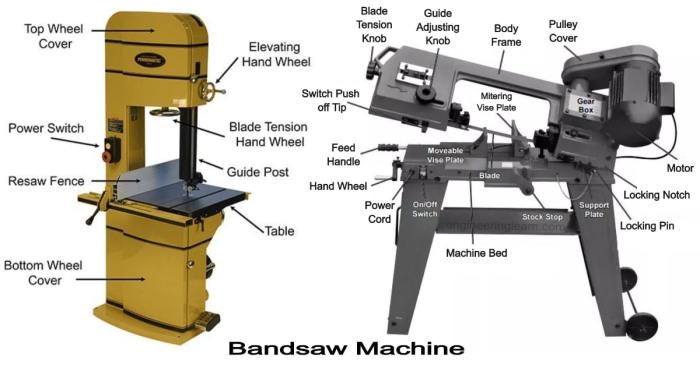
Step into the realm of woodworking precision with our comprehensive guide to the parts of a bandsaw diagram. Embark on a journey that unravels the intricacies of this versatile tool, empowering you to master its functions and unlock its full potential.
From the sturdy frame that anchors the machine to the intricate guides that ensure cutting accuracy, every component plays a vital role in the bandsaw’s symphony of performance. Delve into the details and discover how these parts work together to transform raw lumber into works of art.
Bandsaw Frame
The bandsaw frame is the backbone of the machine, providing structural support and housing the various components that enable the saw to function.
Bandsaw frames are typically made from cast iron, steel, or aluminum, with cast iron being the most common due to its rigidity and vibration dampening properties.
Types of Bandsaw Frames
There are three main types of bandsaw frames:
- C-frame:The most common type of bandsaw frame, featuring a C-shaped design with a vertical column and a horizontal arm.
- Box-frame:A more rigid frame design, consisting of a rectangular box-shaped structure that encloses the blade and other components.
- Parallel-arm frame:A specialized frame design used for cutting large or thick materials, featuring two parallel arms that support the blade.
Bandsaw Table
The bandsaw table is a critical component that supports the workpiece during cutting operations. It provides a stable platform for accurate cuts and allows for adjustments to optimize cutting performance.
Table Adjustments
Bandsaw tables typically offer several adjustments to accommodate different workpiece sizes and cutting requirements. These adjustments include:
- Height adjustment:Adjusts the height of the table to align with the workpiece thickness, ensuring proper blade contact.
- Tilt adjustment:Tilts the table at an angle to facilitate angled cuts, such as miters and bevels.
- Fence adjustment:Positions a fence parallel to the blade, acting as a guide for straight cuts and preventing the workpiece from twisting.
Types of Bandsaw Tables
Bandsaw tables come in various types, each suited to specific applications:
- Cast iron tables:Durable and rigid, providing excellent vibration damping and cutting accuracy.
- Steel tables:Lightweight and less expensive than cast iron, suitable for lighter cutting tasks.
- Composite tables:Combine the advantages of cast iron and steel, offering both durability and weight reduction.
Bandsaw Blade
The bandsaw blade is the heart of a bandsaw, responsible for cutting through various materials. Different types of blades are designed for specific applications, and choosing the right blade is crucial for optimal performance and safety.
Bandsaw blades are typically made of high-carbon steel or alloy steel and are available in various widths, thicknesses, and tooth configurations. The width of the blade determines the maximum cutting depth, while the thickness affects the blade’s rigidity and stability.
Blade Types and Applications
- Skip-tooth blades:Designed for fast, rough cuts in softwood and non-ferrous metals. The large, widely spaced teeth allow for efficient chip removal and reduce blade clogging.
- Hook-tooth blades:Suitable for general-purpose cutting in both softwood and hardwood. The hooked teeth provide a smooth, clean cut but are more prone to clogging than skip-tooth blades.
- Raker-tooth blades:Used for cutting hardwoods and other dense materials. The raker teeth are small and sharp, creating a fine, precise cut with minimal tearing.
- Variable-tooth blades:Combine different tooth configurations along the blade’s length. This allows for versatile cutting in a wide range of materials, from thin metal sheets to thick hardwoods.
Blade Selection Factors
When selecting a bandsaw blade, consider the following factors:
- Material being cut:Different materials require specific tooth configurations and blade widths.
- Cutting speed:The blade’s speed should match the material being cut to prevent premature wear or blade breakage.
- Blade width:The width should be wide enough to handle the cutting depth but narrow enough to avoid excessive blade deflection.
- Tooth pitch:The distance between teeth determines the smoothness of the cut and the rate of chip removal.
Blade Maintenance and Replacement
Proper maintenance is essential for extending the life of a bandsaw blade. Regularly clean the blade with a brush or compressed air to remove sawdust and debris. Inspect the blade for cracks or damage before each use and replace it if necessary.
When replacing a bandsaw blade, ensure it is the correct size and type for the saw. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper installation and tensioning.
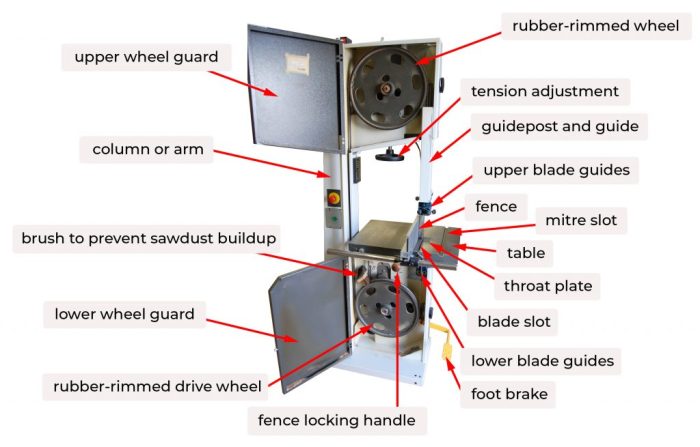
The bandsaw diagram provides a detailed visual representation of the machine’s components. Each part, such as the blade guides, tensioner, and table, plays a crucial role in the bandsaw’s operation. In contrast, the bold monk brewing co. menu offers a tantalizing array of craft beers, from IPAs to stouts, to quench your thirst.
Returning to the bandsaw diagram, the drive wheels ensure smooth blade movement, while the workpiece guides assist in precise cutting.
Bandsaw Wheels
Bandsaw wheels are essential components that guide and drive the bandsaw blade. They are designed to provide support and stability to the blade, ensuring smooth and precise cuts.
Wheel Design
Bandsaw wheels are typically made of cast iron or aluminum. Cast iron wheels are heavier and more durable, while aluminum wheels are lighter and offer better balance. Both types of wheels have a grooved rim that accommodates the bandsaw blade, ensuring proper tracking and preventing slippage.
Wheel Alignment
Proper alignment of the bandsaw wheels is crucial for optimal performance. Misalignment can cause the blade to wander, resulting in inaccurate cuts and potential damage to the blade. To ensure proper alignment, the wheels should be parallel to each other and perpendicular to the table.
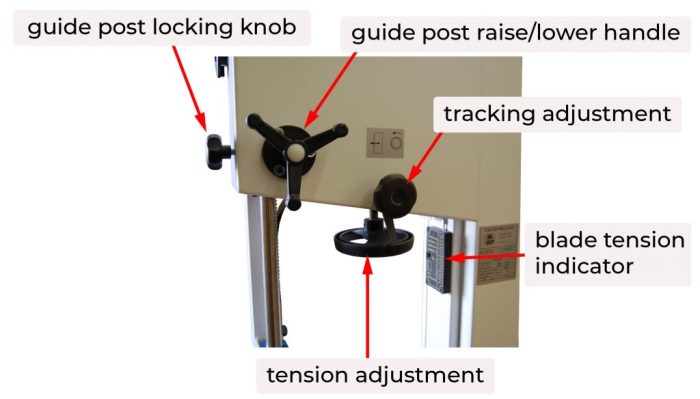
Wheel Tension
Wheel tension is another important factor that affects bandsaw performance. Proper tension keeps the blade taut, preventing it from slipping or breaking. Too little tension can cause the blade to wander, while too much tension can put excessive strain on the blade and bearings.
Bandsaw Guides
Bandsaw guides play a crucial role in maintaining blade stability and preventing it from twisting or derailing during cutting operations. They come in various types, each designed for specific applications.
Types of Bandsaw Guides
- Ball Bearing Guides:These guides utilize ball bearings to reduce friction between the blade and the guide, allowing for smooth and precise cutting.
- Roller Guides:Similar to ball bearing guides, roller guides employ rollers to facilitate blade movement. They offer higher load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Ceramic Guides:Ceramic guides are renowned for their exceptional wear resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures. They are commonly used in demanding environments where blade longevity and precision are paramount.
Importance of Guide Alignment and Adjustment
Proper alignment and adjustment of bandsaw guides are essential for optimal performance. Misaligned guides can cause blade deflection, premature wear, and reduced cutting accuracy. Regular inspection and adjustment of guides ensure that the blade runs straight and true, resulting in clean and precise cuts.
Materials Used for Bandsaw Guides
The material used for bandsaw guides influences their durability, wear resistance, and performance. Common materials include:
- Steel:Steel guides are robust and cost-effective, but they are prone to wear and require frequent replacement.
- Carbide:Carbide guides offer superior wear resistance and durability, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Ceramic:Ceramic guides provide exceptional wear resistance and heat dissipation, extending blade life and enhancing cutting precision.
Bandsaw Fence
A bandsaw fence is a crucial component that helps guide the workpiece during cutting operations, ensuring precise and consistent results. It is typically mounted parallel to the blade and provides a reference surface against which the workpiece is pressed.
There are several types of bandsaw fences, each designed for specific applications:
Rip Fence
- Used for making straight cuts parallel to the edge of the workpiece.
- Typically adjustable to different widths to accommodate varying workpiece sizes.
- May feature scales or indicators for precise positioning.
Miter Fence
- Used for making angled cuts, typically at 45 or 90 degrees.
- Rotates around a pivot point, allowing for precise angle adjustments.
- May have a stop block or other features to ensure repeatable cuts.
Dado Fence
- Used for cutting dadoes, which are slots cut into the workpiece for joinery.
- Consists of two parallel fences that guide the workpiece and determine the width of the dado.
- May have adjustable stops to set the depth of the dado.
To use the bandsaw fence effectively, ensure it is securely attached and parallel to the blade. Adjust the fence to the desired distance from the blade based on the type of cut you want to make. Hold the workpiece firmly against the fence and guide it through the cut, applying even pressure to ensure a clean and accurate cut.
Bandsaw Motor
The bandsaw motor is the powerhouse of the machine, providing the energy to drive the blade and cut through materials. It is typically an electric motor, but some bandsaws may use a gas engine.
There are two main types of motors used in bandsaws: induction motors and universal motors. Induction motors are the most common type, and they are known for their durability and reliability. Universal motors are less common, but they offer higher speeds and are often used in portable bandsaws.
Selecting the Right Motor, Parts of a bandsaw diagram
When selecting a motor for a bandsaw, it is important to consider the following factors:
- The size of the bandsaw
- The type of materials you will be cutting
- The desired cutting speed
For small bandsaws that will be used for cutting light materials, a 1/2-horsepower motor will be sufficient. For larger bandsaws or for cutting thicker materials, a 1-horsepower motor or larger will be required.
Bandsaw Accessories
Bandsaws can be enhanced with a variety of accessories that can improve their performance and versatility. These accessories can help you achieve more precise cuts, work with different materials, and increase your safety while operating the bandsaw.
It is important to use the appropriate accessories for the specific cutting task you are performing. Using the wrong accessories can damage the bandsaw or result in inaccurate cuts.
Types of Bandsaw Accessories
Common bandsaw accessories include:
| Accessory | Function | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Featherboard | Holds the workpiece against the fence and prevents it from moving | Improves cutting accuracy and safety |
| Riving knife | Keeps the workpiece from pinching the blade | Improves safety and prevents kickback |
| Dust collector | Removes sawdust from the cutting area | Improves visibility and reduces dust inhalation |
| Miter gauge | Guides the workpiece for angled cuts | Improves cutting accuracy |
| Blade guides | Keep the blade aligned and prevent it from twisting | Improves cutting accuracy and extends blade life |
Clarifying Questions: Parts Of A Bandsaw Diagram
What are the key components of a bandsaw frame?
The bandsaw frame consists of a rigid structure that supports the entire machine, including the table, blade, and motor. It provides stability and durability during operation.
How does the bandsaw table affect cutting accuracy?
The bandsaw table serves as a stable platform for the workpiece. Its adjustments allow you to set the desired cutting angle and height, ensuring precise and consistent cuts.
What factors should be considered when selecting a bandsaw blade?
When choosing a bandsaw blade, consider the type of material you’ll be cutting, the desired cut quality, and the machine’s capacity. Different blade types and sizes are designed for specific applications.
Why is proper bandsaw wheel alignment crucial?
Proper wheel alignment ensures that the blade runs smoothly and accurately. Misalignment can cause blade wander, vibration, and reduced cutting efficiency.