Reflection refraction diffraction interference practice – Embarking on a journey into the realm of reflection, refraction, diffraction, and interference, this comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of these fundamental optical phenomena. Delving into their applications across diverse fields, from nature to cutting-edge technologies, this exploration illuminates the principles that govern the behavior of light and waves.
As we delve deeper into each phenomenon, we will uncover the laws of reflection, the causes and effects of refraction, the wave properties underlying diffraction, and the fascinating world of interference. Interactive simulations and practice exercises will reinforce understanding, while real-world examples will bring these concepts to life.
Reflection
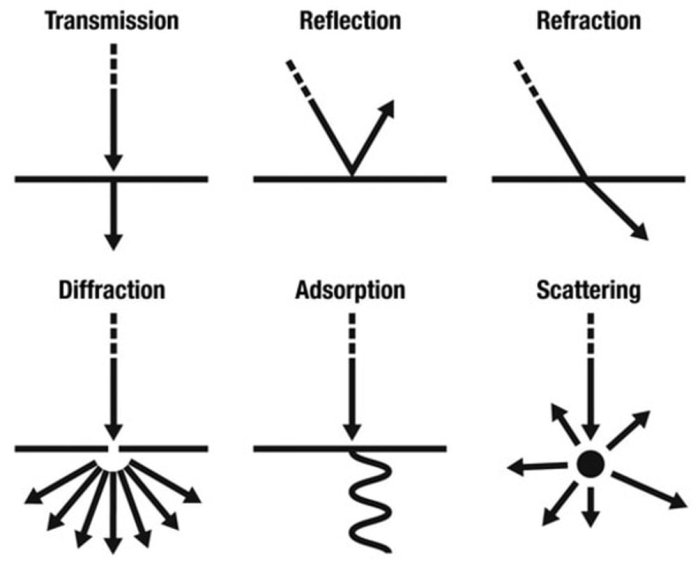
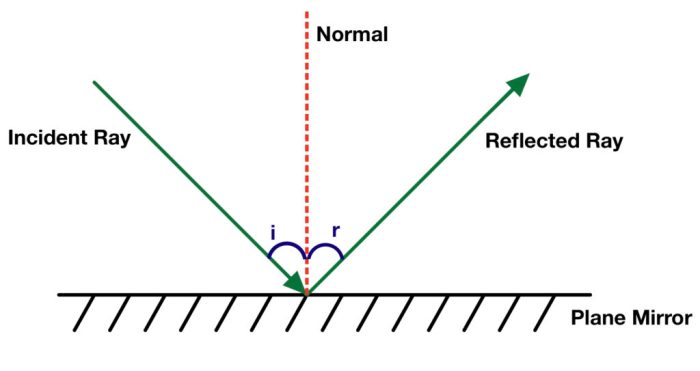
Reflection is the bouncing back of light, sound, or other waves from a surface. It occurs when a wave encounters a boundary between two different mediums, such as air and water, or a solid object and air. The angle at which the wave is reflected is equal to the angle at which it strikes the surface, according to the law of reflection.
Applications of Reflection, Reflection refraction diffraction interference practice
- Mirrors
- Telescopes
- Microscopes
- Radar
- Sonar
Refraction
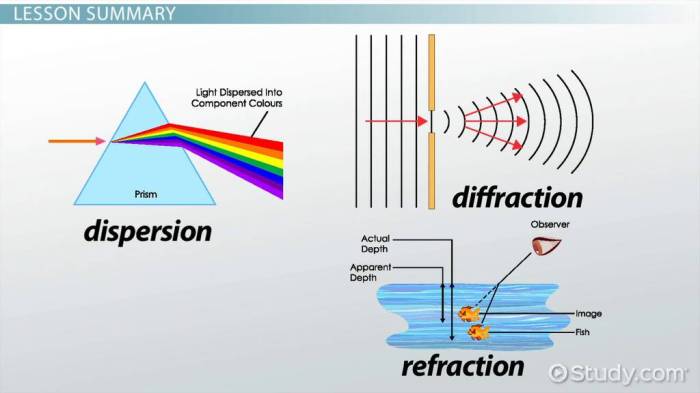
Refraction is the bending of light or other waves when they pass from one medium to another. It occurs because the speed of light is different in different mediums. The angle at which the wave is refracted is determined by the difference in speed between the two mediums and the angle at which the wave strikes the boundary.
Applications of Refraction
- Lenses
- Prisms
- Optical fibers
- Rainbows
- Mirages
Diffraction: Reflection Refraction Diffraction Interference Practice
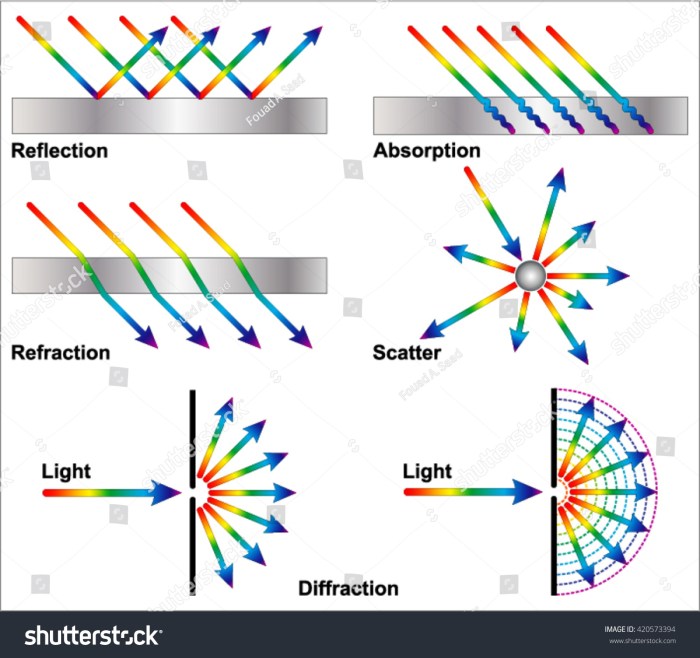
Diffraction is the spreading out of waves as they pass through an aperture or around an obstacle. It occurs because waves have a wave-like nature and tend to spread out as they travel. The amount of diffraction depends on the wavelength of the wave and the size of the aperture or obstacle.
Types of Diffraction
- Single-slit diffraction
- Double-slit diffraction
- Fraunhofer diffraction
- Fresnel diffraction
Interference
Interference is the combination of two or more waves to produce a new wave pattern. It can be constructive, when the waves reinforce each other, or destructive, when the waves cancel each other out. Interference occurs when the waves have the same wavelength and are in phase.
Types of Interference
- Constructive interference
- Destructive interference
- Single-slit interference
- Double-slit interference
General Inquiries
What is the difference between reflection and refraction?
Reflection is the bouncing back of light or waves from a surface, while refraction is the bending of light or waves as they pass from one medium to another.
How does diffraction affect the appearance of objects?
Diffraction causes objects to appear blurry or distorted, as light waves spread out as they pass around the edges of objects.
What is the practical application of interference?
Interference is used in a variety of applications, such as anti-reflection coatings, holography, and optical communication.
