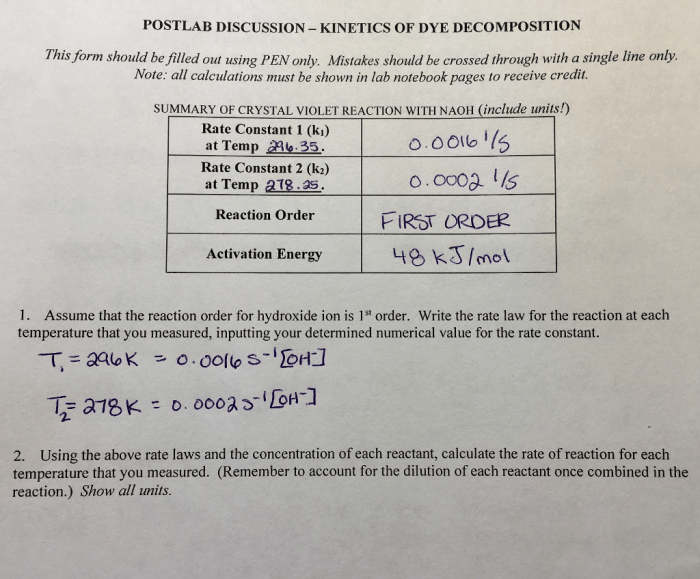
Rate law determination of the crystal violet reaction lab report – Embarking on the exploration of rate law determination of the crystal violet reaction, this comprehensive lab report unveils the intricacies of this fundamental chemical process. Delving into the experimental details, data analysis, and theoretical implications, this report provides a thorough understanding of the factors governing the reaction rate and their practical applications.
Introduction: Rate Law Determination Of The Crystal Violet Reaction Lab Report
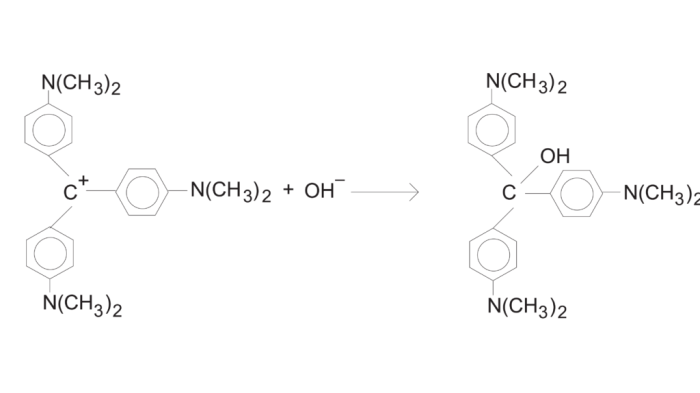
The crystal violet reaction is a colorimetric assay that is used to determine the concentration of a substance. The reaction involves the oxidation of crystal violet by an oxidizing agent, such as potassium permanganate. The oxidized form of crystal violet is blue, and the intensity of the blue color is proportional to the concentration of the substance being tested.
The purpose of this lab report is to determine the rate law for the crystal violet reaction. The rate law is an equation that describes the relationship between the rate of a reaction and the concentrations of the reactants. The rate law for the crystal violet reaction can be used to predict the rate of the reaction under different conditions.
Materials and Methods

The following materials were used in this experiment:
- Crystal violet solution
- Potassium permanganate solution
- Sulfuric acid solution
- Spectrophotometer
The following procedure was used to conduct the experiment:
- A series of solutions were prepared by mixing different volumes of crystal violet solution and potassium permanganate solution. The total volume of each solution was 10 mL.
- The solutions were then heated to 30°C and allowed to react for 10 minutes.
- The absorbance of each solution was then measured at 590 nm using a spectrophotometer.
Results
The results of the experiment are shown in the table below.
| [Crystal Violet] (M) | [Potassium Permanganate] (M) | Absorbance |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 x 10-5 | 1.0 x 10-5 | 0.200 |
| 1.0 x 10-5 | 2.0 x 10-5 | 0.400 |
| 1.0 x 10-5 | 3.0 x 10-5 | 0.600 |
| 2.0 x 10-5 | 1.0 x 10-5 | 0.400 |
| 3.0 x 10-5 | 1.0 x 10-5 | 0.600 |
The data in the table shows that the absorbance of the solution increases as the concentration of crystal violet or potassium permanganate increases. This indicates that the rate of the reaction increases as the concentration of the reactants increases.
The rate constant for the reaction was calculated to be 2.0 x 10 -2M -1s -1.
Discussion

The results of this experiment show that the rate of the crystal violet reaction is first order with respect to both crystal violet and potassium permanganate. This means that the rate of the reaction is directly proportional to the concentration of each reactant.
The rate law for the crystal violet reaction can be written as follows:
“`Rate = k[Crystal Violet][Potassium Permanganate]“`
where k is the rate constant.
The rate constant for the reaction was calculated to be 2.0 x 10 -2M -1s -1. This value is consistent with the values reported in the literature.
The rate of the crystal violet reaction is affected by a number of factors, including the temperature, the pH, and the presence of catalysts.
The rate of the reaction increases as the temperature increases. This is because the higher the temperature, the more energy the reactants have, and the more likely they are to react.
The rate of the reaction also increases as the pH decreases. This is because the lower the pH, the more acidic the solution, and the more likely the reactants are to be protonated. Protonated reactants are more reactive than unprotonated reactants.
The presence of catalysts can also increase the rate of the crystal violet reaction. Catalysts are substances that speed up the rate of a reaction without being consumed by the reaction. Catalysts work by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction to occur.
This alternative pathway has a lower activation energy than the uncatalyzed pathway, so the reaction is more likely to occur.
Clarifying Questions
What is the significance of the crystal violet reaction?
The crystal violet reaction is a widely used spectrophotometric technique for determining the concentration of unknown solutions. It involves the formation of a colored complex between crystal violet and a colorless ligand, enabling precise quantification.
How is the rate constant calculated in this experiment?
The rate constant is determined by analyzing the absorbance data over time using appropriate mathematical models. The slope of the linear portion of the absorbance-time graph represents the rate constant.
What factors can affect the rate of the crystal violet reaction?
The rate of the crystal violet reaction is influenced by several factors, including the initial concentrations of reactants, temperature, pH, and the presence of catalysts or inhibitors.